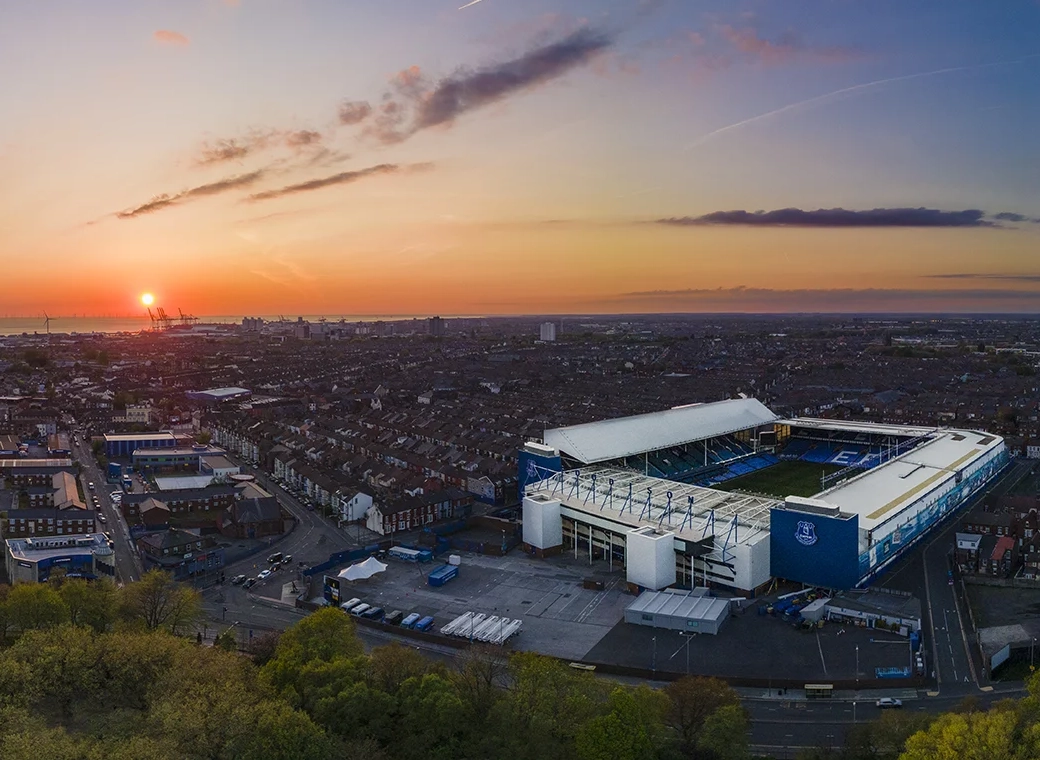
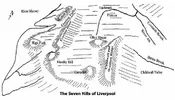
Only 4 yrs after winning the league and only 2 players from that team left Hurst and Royal how sad is that.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Groucho's Fact Hunt
- Thread starter Groucho
- Start date
Some of these aren’t accurate as they claimRandom Facebook copy and paste...
They used to use urine to tan animal skins, so families used to all pee in a pot & then once a day it was taken & sold to the tannery. If you had to do this to survive you were “piss poor.”
But worse than that were the really poor folk who couldn’t even afford to buy a pot; they “didn’t have a pot to piss in” & were the lowest of the low.
The next time you are washing your hands & complain because the water temperature isn’t just how you like it, think about how things used to be. Here are some facts about the 1500s.
Most people got married in June because they took their yearly bath in May, and they still smelled pretty good by June. Since they were starting to smell, however, brides carried a bouquet of flowers to hide the body odor. Hence the custom today of carrying a bouquet when getting married.
Baths consisted of a big tub filled with hot water. The man of the house had the privilege of the nice clean water, then all the other sons and men, then the women, and finally the children. Last of all the babies. By then the water was so dirty you could actually lose someone in it … hence the saying, “Don’t throw the baby out with the Bath water!”
Houses had thatched roofs-thick straw-piled high, with no wood underneath. It was the only place for animals to get warm, so all the cats and other small animals (mice, bugs) lived in the roof. When it rained it became slippery and sometimes the animals would slip and fall off the roof, resulting in the idiom, “It’s raining cats and dogs.”
There was nothing to stop things from falling into the house. This posed a real problem in the bedroom where bugs and other droppings could mess up your nice clean bed, therefore, a bed with big posts and a sheet hung over the top afforded some protection. That’s how canopy beds came into existence.
The floor was dirt. Only the wealthy had something other than dirt, leading folks to coin the phrase “dirt poor.” The wealthy had slate floors that would get slippery in the winter when wet, so they spread thresh (straw) on floor to help keep their footing. As the winter wore on, they added more thresh until, when you opened the door, it would all start slipping outside. A piece of wood was placed in the entrance-way, subsequently creating a “thresh hold.”
In those old days, they cooked in the kitchen with a big kettle that always hung over the fire.. Every day they lit the fire and added things to the pot. They ate mostly vegetables and did not get much meat. They would eat the stew for dinner, leaving leftovers in the pot to get cold overnight and then start over the next day. Sometimes stew had food in it that had been there for quite a while, and thus the rhyme, “Peas porridge hot, peas porridge cold, peas porridge in the pot nine days old.”
Sometimes they could obtain pork, which made them feel quite special. When visitors came over, they would hang up their bacon to show off. It was a sign of wealth that a man could, “bring home the bacon.” They would cut off a little to share with guests and would all sit around and “chew the fat.”
Those with money had plates made of pewter. Food with high acid content caused some of the lead to leach onto the food, causing lead poisoning death. This happened most often with tomatoes, so for the next 400 years or so, tomatoes were considered poisonous.
Bread was divided according to status. Workers got the burnt bottom of the loaf, the family got the middle, and guests got the top, or the “upper crust.”
Lead cups were used to drink ale or whisky. The combination would sometimes knock the imbibers out for a couple of days. Someone walking along the road would take them for dead and prepare them for burial.. They were laid out on the kitchen table for a couple of days and the family would gather around and eat and drink and wait and see if they would wake up, creating the custom of holding a wake.
England is old and small and the local folks started running out of places to bury people. So they would dig up coffins and would take the bones to a bone-house, and reuse the grave. When reopening these coffins, 1 out of 25 coffins were found to have scratch marks on the inside and they realized they had been burying people alive, so they would tie a string on the wrist of the corpse, lead it through the coffin and up through the ground and tie it to a bell. Someone would have to sit out in the graveyard all night (the graveyard shift.) to listen for the bell; thus, someone could be, saved by the bell or was considered a dead ringer.
summerisle
The rain, it raineth every day
summerisle
The rain, it raineth every day
Did You Know, Adolf Hitler's Nephew From Liverpool Fought Against His Uncle In World War II, Earning A Purple Heart In The U.S. Navy. 

William Patrick Hitler was born in Liverpool, England in 1911 to Alois Hitler Jr., Adolf Hitler's half-brother, and an Irish woman named Bridget Dowling.
His father abandoned the family early on, and William later moved to Germany with his mother where he briefly connected with his infamous uncle Adolf as the Nazi party rose to power.
Disillusioned by his uncle's regime and sensing the coming conflict, William and his mother fled to the United States in 1939 where he became a vocal critic of Hitler and the Nazi party.
In a remarkable act of defiance against his own bloodline, William Patrick Hitler enlisted in the U.S. Navy in 1944, serving as a Pharmacist's Mate in the Pacific Theater.
During his service, he was wounded in action and awarded the Purple Heart for injuries sustained while fighting against the very forces aligned with his uncle.
After the war ended, William changed his surname to Stuart-Houston, married Phyllis Jean-Jacques, and settled in Patchogue, New York, where he established a successful blood analysis laboratory.
The couple raised four sons in quiet anonymity, with William seemingly determined to distance himself from his notorious family connection.
William Patrick Hitler, the man who chose to fight against his own uncle's evil empire, passed away on July 14, 1987, taking most of his remarkable story to the grave.

William Patrick Hitler was born in Liverpool, England in 1911 to Alois Hitler Jr., Adolf Hitler's half-brother, and an Irish woman named Bridget Dowling.
His father abandoned the family early on, and William later moved to Germany with his mother where he briefly connected with his infamous uncle Adolf as the Nazi party rose to power.
Disillusioned by his uncle's regime and sensing the coming conflict, William and his mother fled to the United States in 1939 where he became a vocal critic of Hitler and the Nazi party.
In a remarkable act of defiance against his own bloodline, William Patrick Hitler enlisted in the U.S. Navy in 1944, serving as a Pharmacist's Mate in the Pacific Theater.
During his service, he was wounded in action and awarded the Purple Heart for injuries sustained while fighting against the very forces aligned with his uncle.
After the war ended, William changed his surname to Stuart-Houston, married Phyllis Jean-Jacques, and settled in Patchogue, New York, where he established a successful blood analysis laboratory.
The couple raised four sons in quiet anonymity, with William seemingly determined to distance himself from his notorious family connection.
William Patrick Hitler, the man who chose to fight against his own uncle's evil empire, passed away on July 14, 1987, taking most of his remarkable story to the grave.

He’s buried in a cemetery in the middle of Liverpool, his plot is 4 down, 6 across.
The Binman
Player Valuation: £15m
Remarkable that.Did You Know, Adolf Hitler's Nephew From Liverpool Fought Against His Uncle In World War II, Earning A Purple Heart In The U.S. Navy.
William Patrick Hitler was born in Liverpool, England in 1911 to Alois Hitler Jr., Adolf Hitler's half-brother, and an Irish woman named Bridget Dowling.
His father abandoned the family early on, and William later moved to Germany with his mother where he briefly connected with his infamous uncle Adolf as the Nazi party rose to power.
Disillusioned by his uncle's regime and sensing the coming conflict, William and his mother fled to the United States in 1939 where he became a vocal critic of Hitler and the Nazi party.
In a remarkable act of defiance against his own bloodline, William Patrick Hitler enlisted in the U.S. Navy in 1944, serving as a Pharmacist's Mate in the Pacific Theater.
During his service, he was wounded in action and awarded the Purple Heart for injuries sustained while fighting against the very forces aligned with his uncle.
After the war ended, William changed his surname to Stuart-Houston, married Phyllis Jean-Jacques, and settled in Patchogue, New York, where he established a successful blood analysis laboratory.
The couple raised four sons in quiet anonymity, with William seemingly determined to distance himself from his notorious family connection.
William Patrick Hitler, the man who chose to fight against his own uncle's evil empire, passed away on July 14, 1987, taking most of his remarkable story to the grave.
View attachment 314577
Id done a lot of reading regarding war, and have never once heard of this!
Just read this on MSN. 31st of October 2000 was the last day every human being was on planet earth, because on that day 3 cosmonauts blasted off to the iss and there’s been a presence on it ever since.
The last person hanged for Treason in the UK was, as it turned out, the American born son of two naturalised American citizens originally from Ireland.
William Joyce, the man with the famous nickname ‘Lord Haw Haw’, is Britain’s most well-known traitor, of relatively recent times anyway. He had a catchphrase as famous as any comedian’s and to cap it all he had a facial disfigurement in the form of a terrible scar that marked him as a ‘villainous traitor’ as if the words themselves were tattooed across his forehead. Saying all that, a lot of people have argued that he shouldn’t have been convicted of treason at all, let alone be executed for the crime.
On the cold and damp morning of 3 January 1946 a large but orderly crowd had formed outside the grim Victorian prison in Wandsworth. The main gates of London’s largest gaol are situated not more than a few hundred feet from the far more salubrious surroundings of Wandsworth Common in South West London.
Some people had come to protest at what they considered an unjust conviction, while others, ghoulishly and morbidly, wanted to be as close as they could, to what would turn out to be, the execution of the last person to be convicted of treason in this country.
Wandsworth Prison
William Joyce had woken early that morning and although he ate no breakfast he drank a cup of tea. At one minute to nine, an hour later than initially planned, the Governor of Wandsworth Prison came to the condemned man’s cell to inform him that his time had come.
The walk to the adjacent execution chamber was but a few yards but there was just enough time for Joyce to look down at his badly trembling knees and smile. Albert Pierrepoint, the practiced and experienced hangman, said the last words that Joyce would ever hear: ‘I think we’d better have this on, you know’ and placed a hood over the condemned man’s head followed immediately by the noose of the hanging rope.
A few seconds later the executioner pulled a lever which automatically opened the trap door beneath Joyce’s feet. Almost instantaneously Joyce’s spinal cord was ripped apart between the second and third vertebrae and the man known throughout the country as Lord Haw-Haw, was dead.
The gates of HMP Wandsworth around the time of William Joyce's execution
At about the same time as the hangman pulled his deadly lever a group of smartly dressed men in winter coats stepped away from the main crowd outside the gates of the prison and behind some nearby bushes, almost surreptitiously, were seen to raise their right arms in the ‘Heil Hitler!’ salute.
At eight minutes past nine a prison officer came out and pinned an official announcement that the hanging of the traitor William Joyce had taken place. At 1pm the BBC Home Service reported the execution and read out the last, unrepentant pronouncement from the dead man;
William Joyce had actually been born in Brooklyn, New York forty years previously to an English Protestant mother and an Irish Catholic father who had taken United States citizenship. A few years after the birth the family returned to Galway where William attended the Jesuit St Ignatius College from 1915 to 1921. William had always been precociously politically aware but both he and his father, rather unusually for Irish Catholics at the time, were both Unionists and openly supported British rule.
In fact Joyce later said that he had aided and ran with the infamous Black and Tans, the notoriously indisciplined and brutal British auxiliary force sent to Ireland after the First World War in an attempt to help put down Irish nationalism. Joyce actually became the target of an IRA assassination attempt in 1921 when he was just sixteen.
For his own safety William immediately left for England, and after a short stint in the British army (he was discharged when it was found he had lied about his age) he enrolled at Birkbeck College of the University of London where he gained a first but also developed an initial interest in Fascism.
In 1924, while stewarding a Conservative Party meeting at the Lambeth Baths in Battersea, a seventeen year old Joyce was attacked by an unprovoked gang in an adjacent alley-way and received a vicious and deep cut from a razor that sliced across his right cheek from behind the earlobe all the way to the corner of his mouth. After two weeks in hospital he was left with a terrible and disfiguring facial scar. Joyce was convinced that his attackers were ‘Jewish communists’ and the incident became a massive influence on the rest of his life.
The bandage was covering twenty six stiches, he remained in hospital for two weeks
In 1932 Joyce joined Oswald Mosley’s British Union of Fascists and within a couple of years he was promoted to the BUF’s director of propaganda and not long after appointed deputy leader. Joyce was a gifted speaker and for a while became the star of the British fascist movement. He was instrumental in moving the union towards overt anti-semitism – something of which Mosley had always been relatively uncomfortable.
Joyce’s career with the British Union of Fascists only lasted five years when, with membership plummeting, a devastated Joyce was sacked from his paid position in the party by Mosley in 1937.
In late August 1939, shortly before war was declared and probably tipped off by a friend in MI5 that he was about to be arrested, Joyce and his wife Margaret fled to Germany. Joyce struggled to find employment until he met fellow former-Mosleyite Dorothy Eckersley who got him recruited immediately for radio announcements and script writing at German radio’s English service in Berlin.
Crucially this was at a time when his British passport was still valid (although born in New York and brought up in Ireland Joyce had lied about his nationality to obtain a British passport – complications and niceties such as proving one’s identity with a birth certificate weren’t needed at the time) ostensibly to accompany Mosley abroad in 1935.
The infamous nickname of ‘Lord Haw Haw’, associated with William Joyce to this day, was coined by a Daily Express journalist called Jonah Barrington. It’s not widely known but the title was actually meant for someone else completely – almost certainly a man called Norman Baillie-Stewart who had been broadcasting in Germany from just before the war. The nickname referenced Baillie-Stewart’s exaggeratedly aristocratic way of speaking. Barrington had written:
Norman Baillie-Stewart - the real Lord Haw Haw
Baillie-Stewart had already been convicted as a traitor by the United Kingdom for selling military secrets to Germany in the early thirties.
He had the dubious distinction of being the last person in a long line of infamous people to have been imprisoned in the Tower of London for treason.
Late in 1939 when William Joyce had become the more prominent of the Nazi propaganda broadcasters, although at the time no one knew who he was, Barrington swapped the title over to Joyce.
Listening to Lord Haw Haw’s broadcasts (which famously always began with the words “Germany Calling, Germany Calling”) was officially discouraged, although incredibly about 60% of the population tuned in after the BBC news every night. The BBC’s output at the beginning of the war was said to have been exceedingly dreary (plus ca change) and the British public seemed to prefer being shocked rather than bored.
Lord Haw Haw’s over-the-top and sneering attacks on the British establishment were really enjoyed, but in an era of state censorship and restricted information, there was also a desire by listeners to hear what the other side was saying. At the start of the war, simply because there was more to brag about, the German news reports were considered, by some people, to contain slightly more truth than those of the BBC.
As the tide turned in the latter stages of the war Joyce and his wife moved to Hamburg. On the 22nd April 1945 he wrote in his diary:
"Has it all been worthwhile? I think not. National Socialism is a fine cause, but most of the Germans, not all, are bloody fools."
Eight days later, and on the very day that Adolf Hitler and Eva Braun committed suicide in their Berlin Bunker, Joyce made his last drunken broadcast – the remains of his Irish accent can be heard through his slurring voice.
At the end of the war William and his wife Margaret fled to a town called Flensburg near the German/Denmark border and it was there, in a nearby wood, that Joyce was captured by two soldiers. They, like Joyce, were out looking for firewood. Joyce stopped to say hello and one of the soldiers asked “You wouldn’t by any chance be William Joyce, would you?”. To ‘prove’ otherwise, Joyce reached for his false passport and one of the soldiers, thinking he was reaching for a gun, shot him through the buttocks, leaving four wounds.
The arrest was utter poetic justice. The soldier who had shot the infamous broadcaster was called Geoffrey Perry, however, he had been born into a German jewish family as Hourst Pinschewer and had only arrived in England to escape from Hitler’s persecutions. So in the end a German Jew, who had become English had arrested an Irish/American who pretended to be English but had become German.
Back in London, he was charged at Bow Street Magistrates court and in the dock he quietly stated “I have heard the charge and take cognisance of it.” He was subsequently driven to Brixton Prison in a Black Maria and on arrival, he said “So this is Brixton.” “Yes,” retorted his guard, “not Belsen.”
The trial of William Joyce began on 17 september 1945 and for a short period of time, when his American nationality came to light, it seemed that he might be acquitted. “How could anyone be convicted of betraying a country that wasn’t his own?” It was argued. However, the Attorney General, Sir Hartley Shawcross, successfully argued that Joyce’s possession of a British passport (even if he had misrepresented himself to get it) entitled him to diplomatic protection in Germany and therefore he owed allegiance to the King at the time he started working for the Germans.
It was on this contrived technicality that Joyce was convicted of treason on 19th September 1945. The penalty of which, of course, was death.
Sir Hartley Shawcross, he later said that the trial of William Joyce was not one of which he was especially proud
A sizeable minority of the population were uncomfortable with the verdict mainly because of the nationality issue but also because he was alway seen as a bit of a joke-figure rather than someone trying to bring the country down. On Christmas day 1945 an accountant named Edgar Bray wrote to the King:
The historian AJP Taylor made the point that Joyce was essentially hanged for making a false statement on a passport – the usual penalty for which was a paltry fine of just two pounds
William Joyce, the man with the famous nickname ‘Lord Haw Haw’, is Britain’s most well-known traitor, of relatively recent times anyway. He had a catchphrase as famous as any comedian’s and to cap it all he had a facial disfigurement in the form of a terrible scar that marked him as a ‘villainous traitor’ as if the words themselves were tattooed across his forehead. Saying all that, a lot of people have argued that he shouldn’t have been convicted of treason at all, let alone be executed for the crime.
On the cold and damp morning of 3 January 1946 a large but orderly crowd had formed outside the grim Victorian prison in Wandsworth. The main gates of London’s largest gaol are situated not more than a few hundred feet from the far more salubrious surroundings of Wandsworth Common in South West London.
Some people had come to protest at what they considered an unjust conviction, while others, ghoulishly and morbidly, wanted to be as close as they could, to what would turn out to be, the execution of the last person to be convicted of treason in this country.
Wandsworth Prison
William Joyce had woken early that morning and although he ate no breakfast he drank a cup of tea. At one minute to nine, an hour later than initially planned, the Governor of Wandsworth Prison came to the condemned man’s cell to inform him that his time had come.
The walk to the adjacent execution chamber was but a few yards but there was just enough time for Joyce to look down at his badly trembling knees and smile. Albert Pierrepoint, the practiced and experienced hangman, said the last words that Joyce would ever hear: ‘I think we’d better have this on, you know’ and placed a hood over the condemned man’s head followed immediately by the noose of the hanging rope.
A few seconds later the executioner pulled a lever which automatically opened the trap door beneath Joyce’s feet. Almost instantaneously Joyce’s spinal cord was ripped apart between the second and third vertebrae and the man known throughout the country as Lord Haw-Haw, was dead.
The gates of HMP Wandsworth around the time of William Joyce's execution
At about the same time as the hangman pulled his deadly lever a group of smartly dressed men in winter coats stepped away from the main crowd outside the gates of the prison and behind some nearby bushes, almost surreptitiously, were seen to raise their right arms in the ‘Heil Hitler!’ salute.
At eight minutes past nine a prison officer came out and pinned an official announcement that the hanging of the traitor William Joyce had taken place. At 1pm the BBC Home Service reported the execution and read out the last, unrepentant pronouncement from the dead man;
In death, as in this life, I defy the Jews who caused this last war, and I defy the power of darkness which they represent. I warn the British people against the crushing imperialism of the Soviet Union. May Britain be great once again and in the hour of the greatest danger in the west may the Swastika be raised from the dust, crowned with the historic words ‘You have conquered nevertheless’. I am proud to die for my ideals; and I am sorry for the sons of Britain who have died without knowing why.
William Joyce had actually been born in Brooklyn, New York forty years previously to an English Protestant mother and an Irish Catholic father who had taken United States citizenship. A few years after the birth the family returned to Galway where William attended the Jesuit St Ignatius College from 1915 to 1921. William had always been precociously politically aware but both he and his father, rather unusually for Irish Catholics at the time, were both Unionists and openly supported British rule.
In fact Joyce later said that he had aided and ran with the infamous Black and Tans, the notoriously indisciplined and brutal British auxiliary force sent to Ireland after the First World War in an attempt to help put down Irish nationalism. Joyce actually became the target of an IRA assassination attempt in 1921 when he was just sixteen.
For his own safety William immediately left for England, and after a short stint in the British army (he was discharged when it was found he had lied about his age) he enrolled at Birkbeck College of the University of London where he gained a first but also developed an initial interest in Fascism.
In 1924, while stewarding a Conservative Party meeting at the Lambeth Baths in Battersea, a seventeen year old Joyce was attacked by an unprovoked gang in an adjacent alley-way and received a vicious and deep cut from a razor that sliced across his right cheek from behind the earlobe all the way to the corner of his mouth. After two weeks in hospital he was left with a terrible and disfiguring facial scar. Joyce was convinced that his attackers were ‘Jewish communists’ and the incident became a massive influence on the rest of his life.
The bandage was covering twenty six stiches, he remained in hospital for two weeks
In 1932 Joyce joined Oswald Mosley’s British Union of Fascists and within a couple of years he was promoted to the BUF’s director of propaganda and not long after appointed deputy leader. Joyce was a gifted speaker and for a while became the star of the British fascist movement. He was instrumental in moving the union towards overt anti-semitism – something of which Mosley had always been relatively uncomfortable.
Joyce’s career with the British Union of Fascists only lasted five years when, with membership plummeting, a devastated Joyce was sacked from his paid position in the party by Mosley in 1937.
In late August 1939, shortly before war was declared and probably tipped off by a friend in MI5 that he was about to be arrested, Joyce and his wife Margaret fled to Germany. Joyce struggled to find employment until he met fellow former-Mosleyite Dorothy Eckersley who got him recruited immediately for radio announcements and script writing at German radio’s English service in Berlin.
Crucially this was at a time when his British passport was still valid (although born in New York and brought up in Ireland Joyce had lied about his nationality to obtain a British passport – complications and niceties such as proving one’s identity with a birth certificate weren’t needed at the time) ostensibly to accompany Mosley abroad in 1935.
The infamous nickname of ‘Lord Haw Haw’, associated with William Joyce to this day, was coined by a Daily Express journalist called Jonah Barrington. It’s not widely known but the title was actually meant for someone else completely – almost certainly a man called Norman Baillie-Stewart who had been broadcasting in Germany from just before the war. The nickname referenced Baillie-Stewart’s exaggeratedly aristocratic way of speaking. Barrington had written:
A gent I’d like to meet is moaning periodically from Zeesen [the site in Germany of the English transmitter]. He speaks English of the haw-haw, dammit-get-out-of-my-way variety, and his strong suit is gentlemanly indignation.
Norman Baillie-Stewart - the real Lord Haw Haw
Baillie-Stewart had already been convicted as a traitor by the United Kingdom for selling military secrets to Germany in the early thirties.
He had the dubious distinction of being the last person in a long line of infamous people to have been imprisoned in the Tower of London for treason.
Late in 1939 when William Joyce had become the more prominent of the Nazi propaganda broadcasters, although at the time no one knew who he was, Barrington swapped the title over to Joyce.
Listening to Lord Haw Haw’s broadcasts (which famously always began with the words “Germany Calling, Germany Calling”) was officially discouraged, although incredibly about 60% of the population tuned in after the BBC news every night. The BBC’s output at the beginning of the war was said to have been exceedingly dreary (plus ca change) and the British public seemed to prefer being shocked rather than bored.
Lord Haw Haw’s over-the-top and sneering attacks on the British establishment were really enjoyed, but in an era of state censorship and restricted information, there was also a desire by listeners to hear what the other side was saying. At the start of the war, simply because there was more to brag about, the German news reports were considered, by some people, to contain slightly more truth than those of the BBC.
As the tide turned in the latter stages of the war Joyce and his wife moved to Hamburg. On the 22nd April 1945 he wrote in his diary:
"Has it all been worthwhile? I think not. National Socialism is a fine cause, but most of the Germans, not all, are bloody fools."
Eight days later, and on the very day that Adolf Hitler and Eva Braun committed suicide in their Berlin Bunker, Joyce made his last drunken broadcast – the remains of his Irish accent can be heard through his slurring voice.
At the end of the war William and his wife Margaret fled to a town called Flensburg near the German/Denmark border and it was there, in a nearby wood, that Joyce was captured by two soldiers. They, like Joyce, were out looking for firewood. Joyce stopped to say hello and one of the soldiers asked “You wouldn’t by any chance be William Joyce, would you?”. To ‘prove’ otherwise, Joyce reached for his false passport and one of the soldiers, thinking he was reaching for a gun, shot him through the buttocks, leaving four wounds.
The arrest was utter poetic justice. The soldier who had shot the infamous broadcaster was called Geoffrey Perry, however, he had been born into a German jewish family as Hourst Pinschewer and had only arrived in England to escape from Hitler’s persecutions. So in the end a German Jew, who had become English had arrested an Irish/American who pretended to be English but had become German.
Back in London, he was charged at Bow Street Magistrates court and in the dock he quietly stated “I have heard the charge and take cognisance of it.” He was subsequently driven to Brixton Prison in a Black Maria and on arrival, he said “So this is Brixton.” “Yes,” retorted his guard, “not Belsen.”
The trial of William Joyce began on 17 september 1945 and for a short period of time, when his American nationality came to light, it seemed that he might be acquitted. “How could anyone be convicted of betraying a country that wasn’t his own?” It was argued. However, the Attorney General, Sir Hartley Shawcross, successfully argued that Joyce’s possession of a British passport (even if he had misrepresented himself to get it) entitled him to diplomatic protection in Germany and therefore he owed allegiance to the King at the time he started working for the Germans.
It was on this contrived technicality that Joyce was convicted of treason on 19th September 1945. The penalty of which, of course, was death.
Sir Hartley Shawcross, he later said that the trial of William Joyce was not one of which he was especially proud
A sizeable minority of the population were uncomfortable with the verdict mainly because of the nationality issue but also because he was alway seen as a bit of a joke-figure rather than someone trying to bring the country down. On Christmas day 1945 an accountant named Edgar Bray wrote to the King:
I know nothing about Joyce, and nothing about his Politics. I don’t know much about Law either, but I do know enough to be firmly convinced that we are proposing to hang Joyce for the crime of pretending to be an Englishman which crime, so far as I am aware, in no possible case carries a Capital penalty. It happens to be just our bad luck, that Joyce actually WAS an American, (and now IS a German subject), but that is no reason to hang him, because we are annoyed at our bad luck.
The historian AJP Taylor made the point that Joyce was essentially hanged for making a false statement on a passport – the usual penalty for which was a paltry fine of just two pounds
summerisle
The rain, it raineth every day
William Friedkin, director of The Exorcist, used to fire a shotgun to put the willies up the actors on set.

 faroutmagazine.co.uk
faroutmagazine.co.uk

William Friedkin fired a shotgun on the set of ‘The Exorcist’
William Friedkin went to extreme lengths to instil fear in the cast of 'The Exorcist', repeatedly firing a shotgun on the set of the seminal 1973 horror movie.
John from Bootle
Player Valuation: £20m
Matt Le Tissier's highest ever wage was 3.5k p/w  He retired in 2002. To put that in perspective, John Barnes was earning 10k p/w in the early 90's and before that decade was out, Roy Keane was getting 50k p/w
He retired in 2002. To put that in perspective, John Barnes was earning 10k p/w in the early 90's and before that decade was out, Roy Keane was getting 50k p/w
Learned that watching this:
 He retired in 2002. To put that in perspective, John Barnes was earning 10k p/w in the early 90's and before that decade was out, Roy Keane was getting 50k p/w
He retired in 2002. To put that in perspective, John Barnes was earning 10k p/w in the early 90's and before that decade was out, Roy Keane was getting 50k p/wLearned that watching this: